Wildfire prevention is a critical issue, underscored by alarming statistics. The U.S. Forest Service reports that nearly 7.5 million acres are consumed by wildfires annually, with every state at risk.
Tragically, human activity remains the leading cause of these devastating fires, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive prevention strategies.Among the various approaches to controlling wildfires, the most effective method is prevention at its source.
Proactive forest and agricultural management plans, coupled with heightened public awareness and a shared sense of responsibility, play pivotal roles in reducing the frequency and severity of these disasters.
By prioritizing prevention and fostering a collective commitment to safeguarding our environment, we can minimize the risk of catastrophic wildfires.
Read More: Top Strategies for Forest Fire Prevention
Weather Conditions:
Weather conditions significantly impact the likelihood and severity of wildfires. High temperatures, strong winds, and prolonged dry spells create an ideal environment for fires to ignite and spread quickly.
Dry vegetation becomes highly combustible under such conditions, with even the smallest spark potentially leading to a devastating blaze. Strong winds can carry embers over long distances, fueling the rapid spread of fires across vast areas.
Seasonal weather patterns, such as heatwaves or droughts, increase wildfire risks, making proactive monitoring and preparedness essential.

Communities, emergency services, and local authorities must closely track weather forecasts during fire-prone seasons, implementing preventive measures such as fire bans or restrictions to reduce the likelihood of wildfires.
Keep Vehicles off Dry Grass and Leaves:
Parking vehicles on dry grass or leaves during hot, dry weather significantly increases the risk of starting a wildfire.
The heat generated from a vehicle’s exhaust system or catalytic converter can ignite dry vegetation, especially in areas where grass and leaves have become parched due to lack of rain.
In particular, vehicles with hot exhaust pipes can cause sparks to fly, further heightening the fire danger. This risk is often underestimated, but it can lead to disastrous consequences.
To mitigate this threat, it’s crucial to park vehicles on paved or gravel surfaces, away from dry grass, particularly during fire season. Public awareness campaigns can help reduce these avoidable fire risks.
Equipment and Sparks:
Various types of equipment, such as lawnmowers, chainsaws, and other machinery, pose a significant fire risk when used in dry conditions.
Sparks from equipment can easily ignite dry grass, leaves, or brush, leading to uncontrolled fires. In agricultural and industrial settings, this risk is particularly concerning, as large machines are often used near flammable vegetation.
Regular maintenance of equipment, including checking spark arrestors and ensuring that no fuel leaks are present, can help reduce the chance of ignition.

Additionally, operating machinery during cooler parts of the day when conditions are less favorable for fires and keeping a fire extinguisher nearby are important precautionary measures to minimize the risk of fires caused by equipment.
Wildfires Caused by Agricultural Activities:
Agricultural activities are a common cause of wildfires, with both intentional and unintentional factors contributing to the risk. Controlled burns, commonly used to clear fields, can easily spiral out of control if weather conditions change unexpectedly.
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and combines, can also emit sparks that ignite dry grass or crops. Improper disposal of crop residues or debris can further contribute to fire hazards.
Farmers and landowners must implement proper fire safety protocols, such as creating firebreaks, monitoring weather conditions closely, and using equipment designed to minimize sparks.

Adhering to local regulations and seeking advice on safe burning practices can also help prevent agricultural activities from leading to devastating wildfires.
Forest Fire Prevention and EOSDA Forest Monitoring:
The prevention and early detection of forest fires are significantly enhanced through the use of advanced technologies such as EOSDA Forest Monitoring.
This system employs satellite imagery and remote sensing data to monitor forest health and detect early signs of fire risks.
By tracking temperature fluctuations, vegetation moisture levels, and other environmental factors, EOSDA helps predict potential fire outbreaks.
This proactive approach allows authorities to respond rapidly to emerging threats, potentially preventing the spread of fires. Additionally, forest monitoring data can inform strategic decisions for fire management and forest conservation.
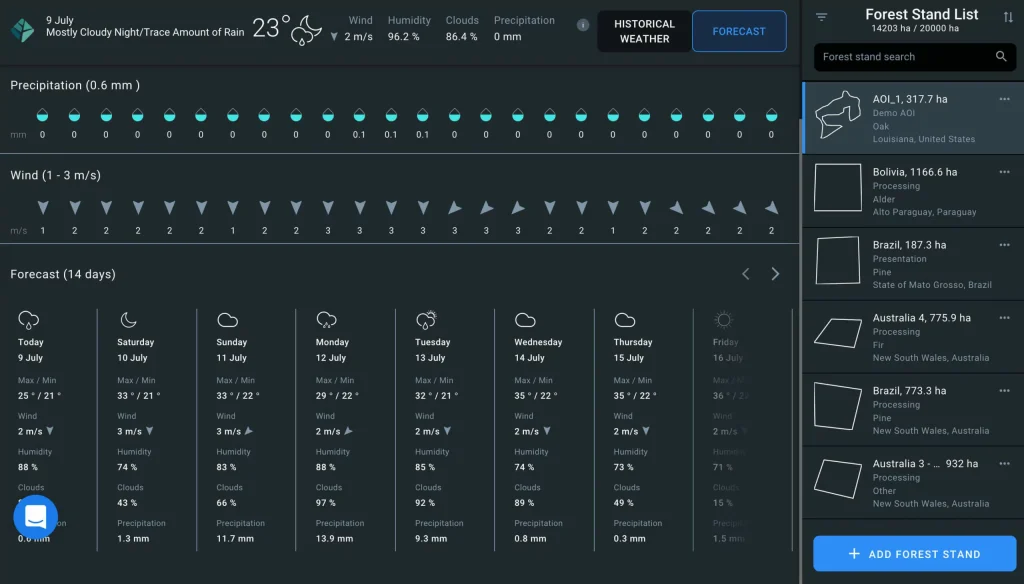
As wildfires become more frequent, adopting advanced monitoring systems like EOSDA will play a crucial role in safeguarding forests and mitigating fire risks.
Caution Notes for General Public:
The general public plays an essential role in preventing wildfires, especially during periods of high fire risk.
Simple actions, such as ensuring campfires are fully extinguished before leaving, properly disposing of cigarette butts, and avoiding outdoor burning in dry conditions, can make a big difference in reducing fire risks.
Additionally, people should stay informed about fire restrictions in their area, avoid using equipment that could spark fires during dry periods, and report any suspicious activity near forested or grassland areas.
Educating children and adults about fire safety and the potential consequences of their actions is critical.

By adopting responsible behaviors and staying alert, the public can help protect communities and natural landscapes from the devastating impact of wildfires.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main causes of wildfires?
Wildfires can be caused by natural factors such as lightning, but human activity is the leading cause. This includes discarded cigarette butts, campfires left unattended, sparks from machinery, and intentional arson. Weather conditions, such as dry, hot spells and strong winds, can also contribute to the spread of wildfires.
How can I prevent a wildfire from starting in my area?
To prevent wildfires, avoid parking vehicles on dry grass, maintain equipment to prevent sparks, and ensure campfires are fully extinguished. Be mindful of local fire restrictions, and report any suspicious activity that could lead to fires. Creating defensible spaces around homes and practicing safe burning techniques also help prevent wildfires.
What role does weather play in wildfire prevention?
Weather, especially high temperatures, dry conditions, and strong winds, significantly affects the likelihood of a wildfire. Hot, dry conditions create ideal environments for fires to start and spread quickly. Monitoring weather forecasts and restricting outdoor activities during high-risk periods can reduce the chances of wildfires igniting.
Why is it dangerous to park vehicles on dry grass?
Parking vehicles on dry grass or leaves can be dangerous because the heat from the exhaust system may ignite the vegetation beneath. Even a small spark from the exhaust can set dry grass on fire. It’s essential to park vehicles on paved or gravel surfaces, especially during dry conditions.
How does equipment cause wildfires?
Equipment like lawnmowers, chainsaws, and agricultural machinery can cause wildfires when they emit sparks or generate heat that ignites dry vegetation. Regular maintenance and ensuring equipment is in good working order, especially the spark arrestors, can help minimize the risk of fire caused by machinery.
What is EOSDA Forest Monitoring and how does it help prevent wildfires?
EOSDA Forest Monitoring is a satellite-based system that tracks real-time forest health and detects early signs of fire risks. By analyzing environmental conditions, including temperature, vegetation moisture, and overall forest health, EOSDA helps predict and identify potential wildfire outbreaks, enabling early intervention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wildfire prevention is a shared responsibility that requires proactive efforts from individuals, communities, and authorities alike. By understanding the causes and risks of wildfires—ranging from weather conditions to human activities—we can implement effective strategies to mitigate their impact.