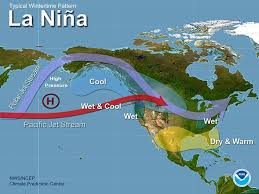
La Niña and El Niño, two opposing phases of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), are driven by shifts in Pacific Ocean temperatures. La Niña cools surface waters, leading to more frequent hurricanes in the Atlantic, droughts in the southern U.S., and wet conditions in Southeast Asia.
In contrast, El Niño warms the waters, causing drier weather in Southeast Asia and Australia, while increasing rainfall across southern U.S. and South America.
As climate change accelerates, these natural cycles are expected to intensify and become more unpredictable. Warmer global temperatures will amplify the impacts of both phases, resulting in more extreme weather events, such as worsening droughts, floods, and wildfires.
This unpredictability challenges preparedness and adaptation, impacting agriculture, infrastructure, and ecosystems worldwide.
Read More: How Will La Niña and El Niño Affect Weather Patterns in 2024?
El Niño’s Impact in 2024
In 2024, the transition from La Niña to El Niño marked a significant shift in global weather patterns, triggering a range of extreme climate events across continents.
These changes not only underscored the powerful influence of El Niño but also emphasized the increasing volatility of weather systems under climate change.
North America: Relief and Risk
In the United States, El Niño brought a dramatic reversal of drought conditions across the Southwest.
California, after enduring years of dry spells, received substantial rainfall, helping to replenish reservoirs and improve water supplies. However, this relief came at a cost: widespread flooding and destructive mudslides occurred due to the soil’s diminished ability to absorb water after prolonged drought.
Simultaneously, states like Texas and Louisiana faced a different set of challenges. El Niño contributed to record-breaking heatwaves and prolonged dry conditions, intensifying the risk of wildfires and placing strain on energy and water resources.
Meanwhile, the Midwest and Northeast experienced cooler and wetter-than-average summers, causing agricultural delays and crop disruptions.
A Surprising Hurricane Season in Florida
Typically, El Niño suppresses Atlantic hurricane activity by increasing wind shear in the tropical Atlantic. However, 2024 defied expectations. Florida saw an unusually active hurricane season, driven by two key factors:
- Record-High Ocean Temperatures: Atlantic sea surface temperatures reached unprecedented levels, providing ample energy for storm development and intensification.
- Delayed Wind Shear Effects: Though El Niño conditions were present, the associated increase in wind shear arrived late, allowing early-season storms to form and strengthen.
- As a result, more hurricanes made landfall than typically expected during an El Niño phase, bringing significant damage and testing emergency preparedness across the Southeast.
Global Implications of the 2024 El Niño
The effects of El Niño in 2024 were not limited to North America. Around the globe, this climatic shift led to:
- Intense droughts in Southeast Asia and Australia
- Excessive rainfall and flooding in parts of South America
- Temperature anomalies affecting ecosystems and food security worldwide
This transition revealed the interconnectedness of Earth’s climate systems and highlighted how a single oceanic event can ripple through agriculture, infrastructure, and economies across continents.
Looking Ahead: El Niño’s Continuation into 2025
With El Niño expected to persist into 2025, the risks of amplified weather extremes are likely to grow. Regions across the globe will need to enhance their climate resilience, adapting infrastructure, disaster response systems, and agricultural strategies to manage the increasing uncertainty.
As climate change continues to interact with natural patterns like El Niño and La Niña, understanding these phenomena becomes more critical than ever. Governments, industries, and communities must stay alert, informed, and prepared for a future where climate unpredictability may become the new norm.
Frequent Asked Question (FAQs)
What is El Niño?
El Niño is a climate pattern marked by warmer Pacific Ocean waters, causing global shifts in temperature, rainfall, and storm activity.
How did El Niño affect the U.S. in 2024?
It brought heavy rain to the Southwest, heatwaves to the South, and cooler, wetter conditions to the Midwest and Northeast.
Why were there so many hurricanes in Florida in 2024?
Despite El Niño, warm Atlantic waters and weakened wind shear early in the season fueled more storms than expected.
Will El Niño continue into 2025?
Yes, current projections indicate El Niño will persist into 2025, possibly increasing extreme weather events.
How does climate change influence El Niño?
Climate change may intensify El Niño’s effects, making weather patterns more extreme and less predictable.
Conclusion
The events of 2024 have shown that El Niño is no longer just a seasonal anomaly — it’s a global force with increasingly complex consequences. From reversing droughts in the U.S. Southwest to intensifying hurricane threats in Florida, this year’s El Niño demonstrated how interconnected and unpredictable our climate systems have become.